Diabetic Neuropathy
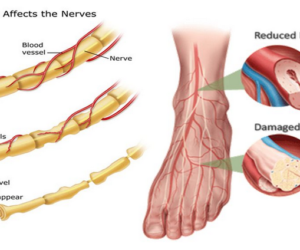
Diabetic neuropathy is a progressive functional loss of nerve fiber, often damages legs and feet nerves. It is seen as common complication in 50% of diabetes mellitus patients.
Overview
Depending on which type of nerve affected, it can range the symptoms of mild pain to severe damage affecting the other parts of body. It can be any of four types developing gradually from mild unnoticing symptoms to severe painful, disabling problem which can even lead to fatal.
Causes:
- Damage to nerves and blood vessels due to prolonged diabetes.
- Inflammation in the nerves due to autoimmune response.
- Genetic factors.
- Smoking and alcohol abuse.
Risk Factor
The major risk factor for neuropathy is diabetes, making more susceptible to nerve damage.
Other factors are
- Poor blood sugar control
- Any Kidney disease
- Being overweight
- Smoking
- Symptoms
Types Peripheral neuropathy Autonomic neuropathy Diabetic amyotrophy mononeuropathy
Most common type.
Symptoms are worse at night
It affects autonomic systems of body
Also known as radiculoplexus neuropathy,femoral neuropathy.
More common in with type 2 diabetes and older adults.
Usually affects on one side of body and improve partial over time
Also known as focal neuropathy,
It’s most common in older adults.
Symptom starts all of sudden which causes severe pain. But it diminishes over few weeks by itself without causing long term problems.
Affected areas feet and legs are often affected first, followed by hands and arms. Mostly affecting heart, bladder, lungs, stomach, intestines, sex organs and eyes affects nerves in the thighs, hips, buttocks or legs It involves damage to a specific nerve of face, torso or leg.
Symptoms Neurological deficits like numbness, hypersensitivity to touch, sharp pains and cramps, weakness, loss of reflexes, balance and coordination, serious foot problems like ulcers, deformities, infections
- Hypoglycemia unawareness, bladder problems, Constipation, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, Difficulty in swallowing, genital problems, postural hypotension.
- Sudden, severe pain and weakness in affected area, difficulty to stand from sitting position, Abdominal swelling, Weight loss
- Pain in affected nerve. Eye problems, Bell’s palsy.
A common type of compression neuropathy in people with diabetes is carpal tunnel syndrome.
Complications
- Charcot joint in foot resulting in swelling, instability and deformity
- Urinary tract infections and urinary incontinence.
- Hypoglycemia unawareness
- Low blood pressure.
- Digestive problems.
- Sexual dysfunction.
- Increased or decreased sweating.
Prevention
Blood sugar control
Continuous monitoring of blood sugar is important.
Frequent doses of medication to be taken.
The American Diabetes Association recommends that people with diabetes have a blood test called the A1C test at least twice a year to find out your average blood sugar level for the past two to three months.
If your blood sugar isn’t well-controlled or you change medications, you may need to get tested more often.
Foot care
Have a comprehensive foot exam at least once a year, having your doctor check your feet at each office visit
Check your feet every day.
Regularly look for blisters, cuts, bruises, cracked and peeling skin, redness and swelling.
Feet should be maintained clean and dry which can be done by washing with lukewarm water and mild soap every day and drying it carefully by patting with soft towel. Do not soak feet for long time in water.
Moisturize your feet thoroughly to prevent cracking.
Trim your toenails carefully.
Wear clean, dry socks: Look for socks made of cotton or moisture-wicking fibers that don’t have tight bands or thick seams.
Wear cushioned shoes that fit well: A podiatrist can teach you how to buy properly fitted shoes and to prevent problems such as corns and calluses.
Physiotherapeutic Management of Pain In Diabetic Neuropathy
Physiotherapy is an effective treatment that can help restore balance and sensation that has been lost and regain motions while walking.
Exercising is a free, easy method of preventing this aggravating health condition.
Strengthening of weak muscles
Improving range of motion by reducing stiffness.
Modalities like Transcutaneous Nerve Stimulation (TENS), Static magnetic field therapy, Low-intensive laser therapy, Monochromatic infrared light are effective in neuropathy.
Exercises that help to learn over maneuver surfaces, stand without getting dizzy and maintaining balance.
Resensitization techniques to improve loss of senses in hand and foot.
Aerobic exercise alone has the power to guard diabetics against peripheral neuropathy.
Taking regular, brisk walks “improved nerve conduction velocity and decreased incidence of motor and sensory peripheral neuropathy” in diabetics.
Check out these links for relevant information : Neurological physiotherapy
For more details contact us on 📞9618906780
